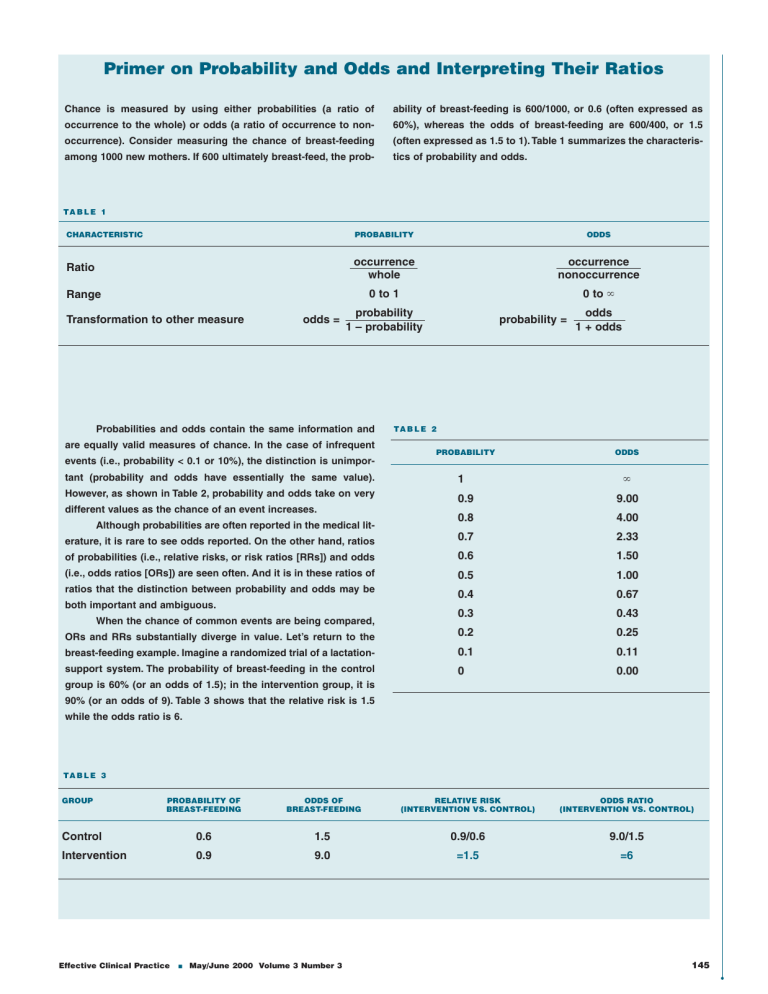
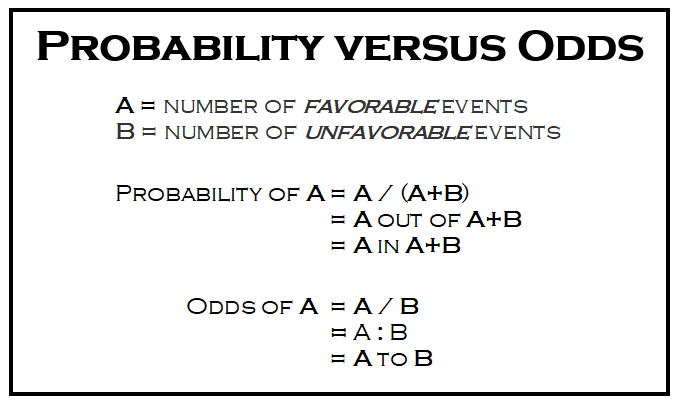
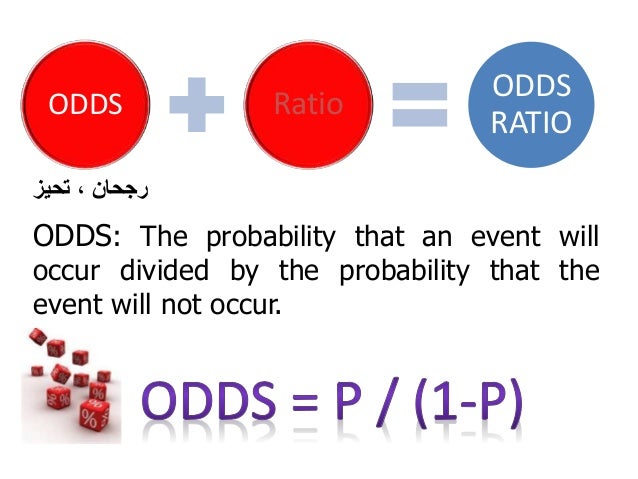
Converting between odds and probability is straightforward To convert from a probability to odds, divide the probability by one minus that probability So if the probability is 10% or 010, then the odds are 01/09 or '1 to 9' or 0111 To convert from odds to a probability, divide the odds by one plus the oddsWhen probability =1, it is definite Odds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probability that it doesn't occur is 1 to 3 against

Example 8 29 Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios R Bloggers
Is a higher odds ratio better
Is a higher odds ratio better-For instance, a probability of 075 is the same as 31 odds â ¦ Fractional odds are sometimes called British odds or traditional odds and are sometimes written as a fraction, such as 6/1, or expressed as a ratio, like sixtoone Some people call the odds the odds ratio because the odds itself is a ratio A study in the New England Journal of Medicine reported racial differences in referralsThe odds of winning are 1/9,999 () and the probability of winning is 1/10,000 () In this case, odds and probability are essentially identical Relative Risk (RR) & Odds Ratio (OR) The difference between odds and probability is important because Relative Risk is calculated with probability and Odds Ratio is calculated with odds




Into The Logistic Regression Towards Ai The Best Of Tech Science And Engineering
Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three common, but often misused, statistical measures in clinical research In this paper, the authors dissect what each of these terms define, and provide examples from the medical literature to illustrate each of these statistical measures Finally, the correct and incorrect methods to use these measures are summarized Adjusted odds ratio vs odds ratio When Odds ratio is above 2, then it is simply put as XX times higher likelihood (XX=odds ratio) If odds ratio is 25, then there is a 25 times higher likelihood of having the outcome compared to the comparison group From the above example, one might say "The odds of having a postoperative infection is 35 times higher if the The odds are defined as the probability that the event will occur divided by the probability that the event will not occur If the probability of an event occurring is Y, then the probability of the event not occurring is 1Y (Example If the probability of an event is 080 (80%), then the probability that the event will not occur is 1080 = 0, or %
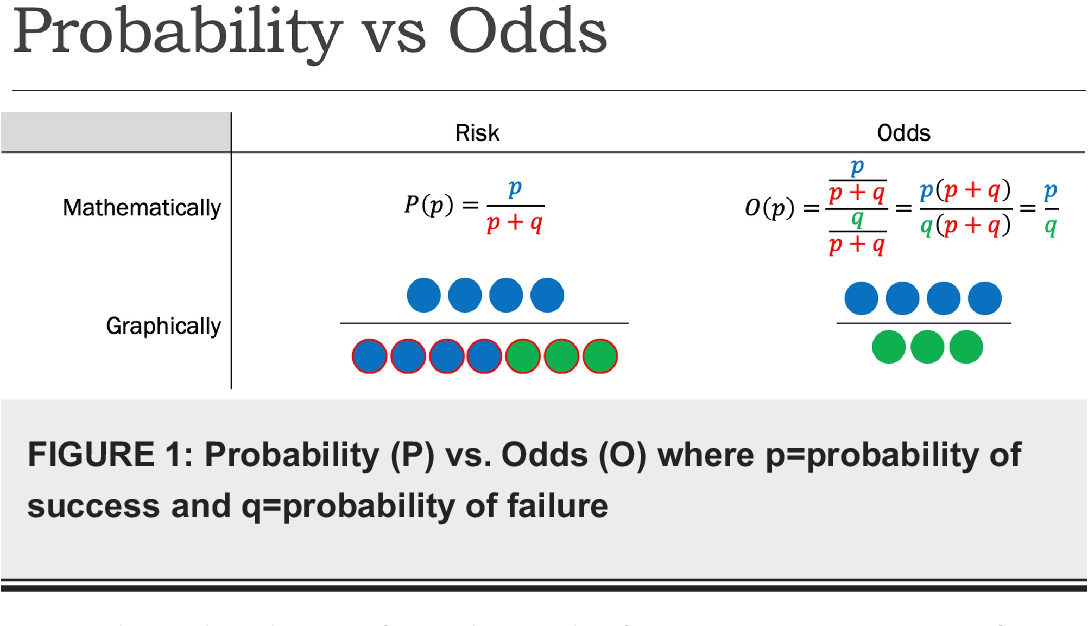
Odds are bound between 0 and positive infinity That is, you can have the odds of 0100 (not gonna happen), or (10thousand times more likely to happen than not) There are no negative odds Probability is bound between 0 and 1 That is, when probability = 0, an event is impossible;(5) At concentrations below the respective median for each variable, odds ratios of between 142 and 167 were calculated whereas at concentrations above the respective medians the odds ratios ranged from 450 to 633 (P less than 0001)Odds range from 0 to infinity, while probabilities range from 0 to 1, and hence are often represented as a percentage between 0% and 100% reversing the ratio switches odds for with odds against, and similarly probability of success with probability of failure
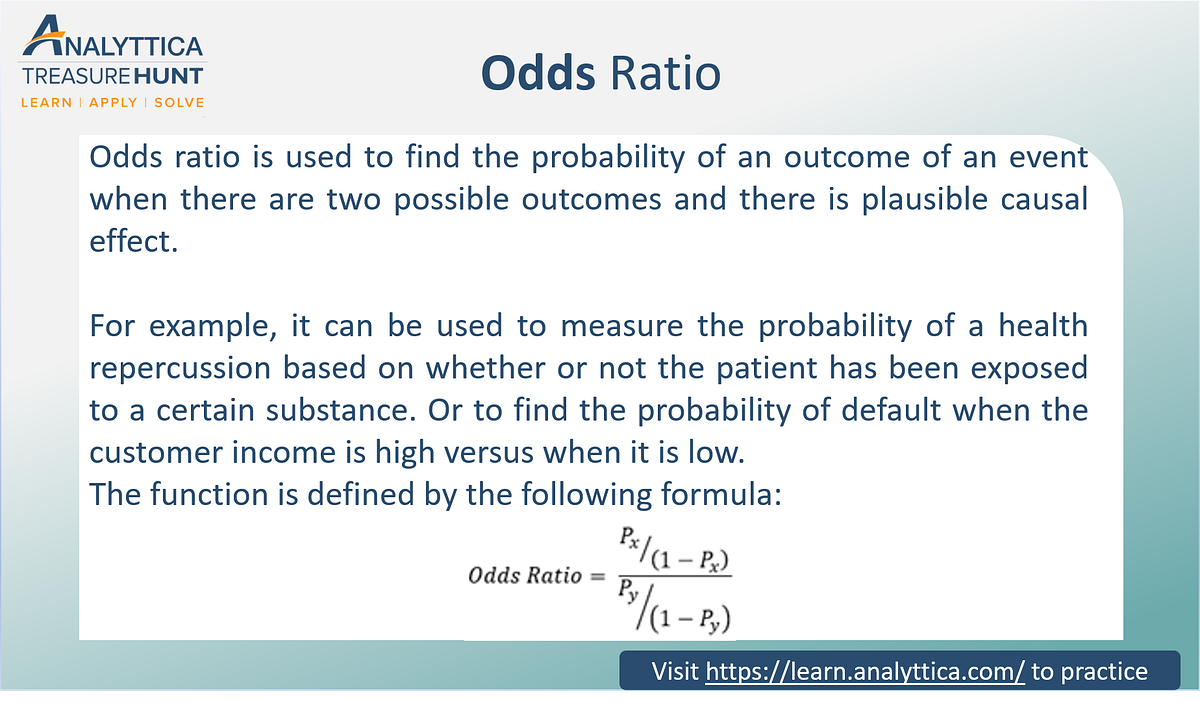
How to find probability and odds and the difference between the two We also discuss experimental probablility, theoretical probability, odds in favor, andOdds ratio is the likelihood that an event will occur in relation to the likelihood that an event will not occur, 1 event for and 5 events against In Gambling, the "odds" are a ratio of the likelihood of a certain outcome, related to the other outcomes I had to look this up, because I forgot this part of finite math, from 25 years agoP (Event) P (Event c) ⇒ Odds in Favor of an Event = P (Event) P (Event c) Probabilities against and for the event can be used as the antecedent and consequent of the ratio representing the odds against an event in place of unfavorable and favorable choices



Primer On Probability And Odds And Interpreting Their Ratios



Are You Mixing Up Odds With Probability By Keith Mcnulty Towards Data Science
Difference Between Probability and Odds • Probability is expressed as a number between 0 and 1, while Odds is expressed as a ratio • Probability ensures that an event will occur, but Odds is used to find out whether the event will ever occur R Calculate And Interpret Odds Ratio In Logistic Regression Stack Overflow What is the difference between odds and chances What is the difference between odds and chances Odds are always larger then probability , since 1Prob(A)1018 3 Odds Ratio = Odds(Group 1)/ Odds(Group 2) Interpretation;It will come up heads 50% of the time, making the probability of it happening 05 (50% of 1) This makes the odds of it happening 10 (50÷50)



Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium



Log Odds Definition And Worked Statistics Problems
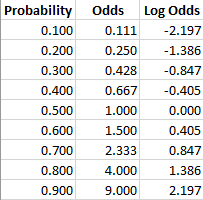
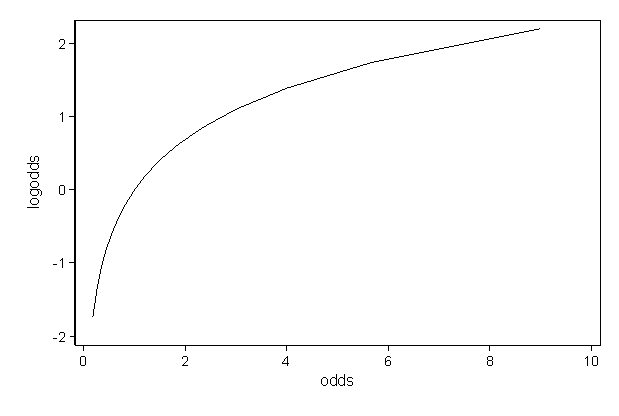
But when p is not small, the probability and odds will generally be quite different For example if p=05, we have odds=05/05=1 As p increases, the odds get larger and larger For example, with p=099, odds=099/001=99The odds ratio An odds ratio (OR) is a measure of association between an exposure and an outcome In a casecontrol study you can compare the odds that those with a disease will have been exposed to the risk factor, with the odds that those who don't have the disease or condition will have been exposed To find the odds against us, simply flip the ratio of odds in favor of winning 1 2 becomes 2 1 If you express the odds against winning as a fraction, you get 2/1 Remember, as above, that this isn't an expression of how likely you are to lose, but rather the ratio of unfavorable outcomes to favorable outcomes



Odds Vs Probability Vs Chance Data Science Central



Ppt Conditional Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Odds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 – A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probability that it doesn't occur is 1 to 3 against 1 Probability = Event/Sample Space 2 Odds= Prob (Event)/Prob (NonEvent) 3 Odds Ratio = Odds (Group 1)/ Odds (Group 2) Interpretation The Odds Ratio is a measure of association between exposure and outcome OR=Odds (Group 1)/Odds (Group2)>1 indicates the increased occurrence of an event in Group 1 compared to Group 2Odds (Safety) = 12/72 = 1787 Now get out your calculator, because you'll see how these relate to each other Odds (Accident) = Pr (Accident)/Pr (Safety) = 053/947 Understanding Probability, Odds, and Odds Ratios in Logistic Regression Despite the way the terms are used in common English, odds and probability are not interchangeable



9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
The probability that an event will occur is the fraction of times you expect to see that event in many trials Probabilities always range between 0 and 1 The odds are defined as the probability that the event will occur divided by the probability that the event will not occur Why do we use odds Odds can have any value from zero to infinity and they represent a ratio of desired outcomes versus the field Odds are a ratio, and can be given in two different ways 'odds in favor' and 'odds against' 'Odds in favor' are odds describing the if an event will occur, while 'odds against' will describe if an event will not occurAs nouns the difference between odds and rate is that odds is the ratio of the probabilities of an event happening to that of it not happening while rate is (obsolete) the estimated worth of something;




How To Place Odds Ratio Of Y Value At One Standard Deviation Above And Below Mean Of X To A Ggplot Or Other R Plot Stack Overflow




Into The Logistic Regression Towards Ai The Best Of Tech Science And Engineering
Fractional odds are sometimes called British odds or traditional odds and are sometimes written as a fraction, such as 6/1, or expressed as a ratio, like sixtoone Decimal odds represents theIn this case, the odds ratio equals one, and conversely the odds ratio can only equal one if the joint probabilities can be factored in this way Thus the odds ratio equals one if and only if X and Y are independent Recovering the cell probabilities from the odds ratio and marginal probabilities The difference between the payoff odds and the odds of the bet winning is where the house edge stems from In other words, the casino has shaved off a little bit of the probability so that it makes a slight profit on the odds
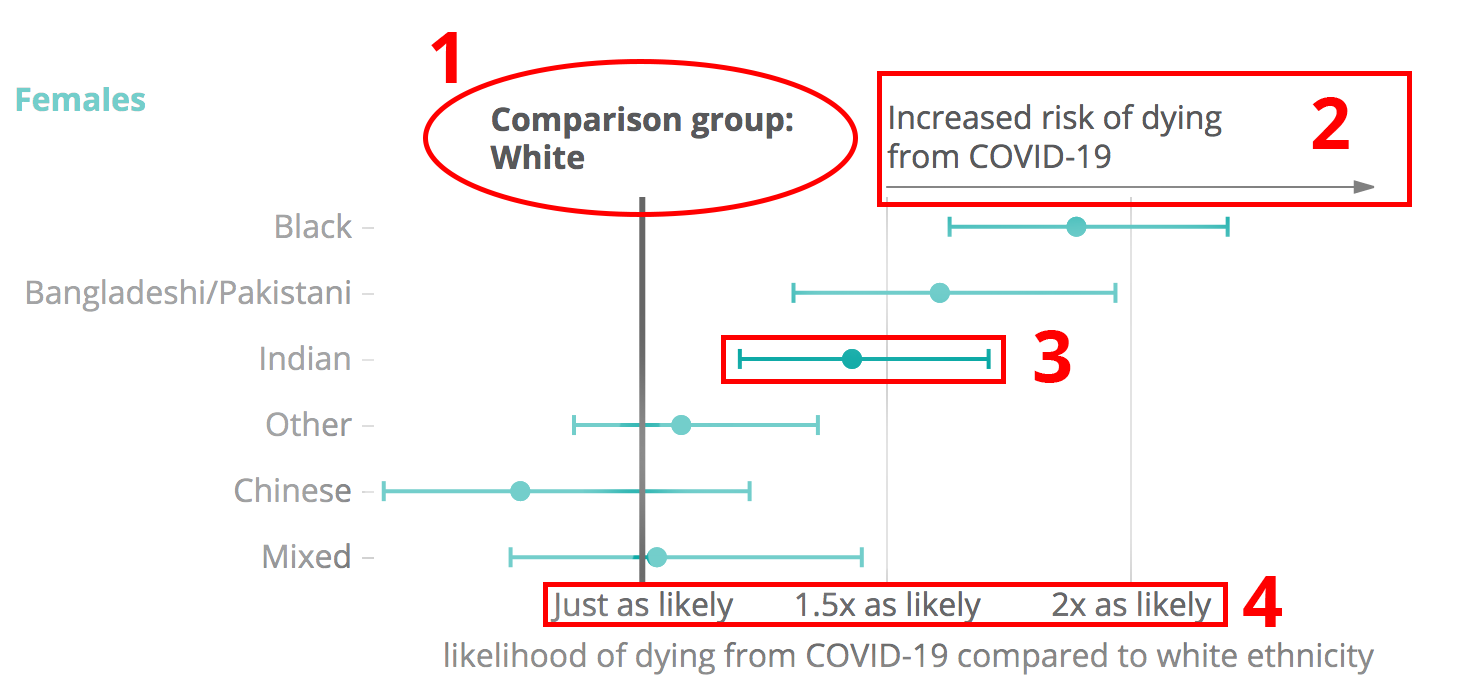



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download
Value As a verb rate is to assign or be assigned a particular rank or level or rate can be to berate, scoldMany people wrongfully assume odds and probabilities are the same thingThey're definitely not, as there's a significant difference between saying there areRather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsterm




Odds Ratios The Odd One Out Stats By Slough
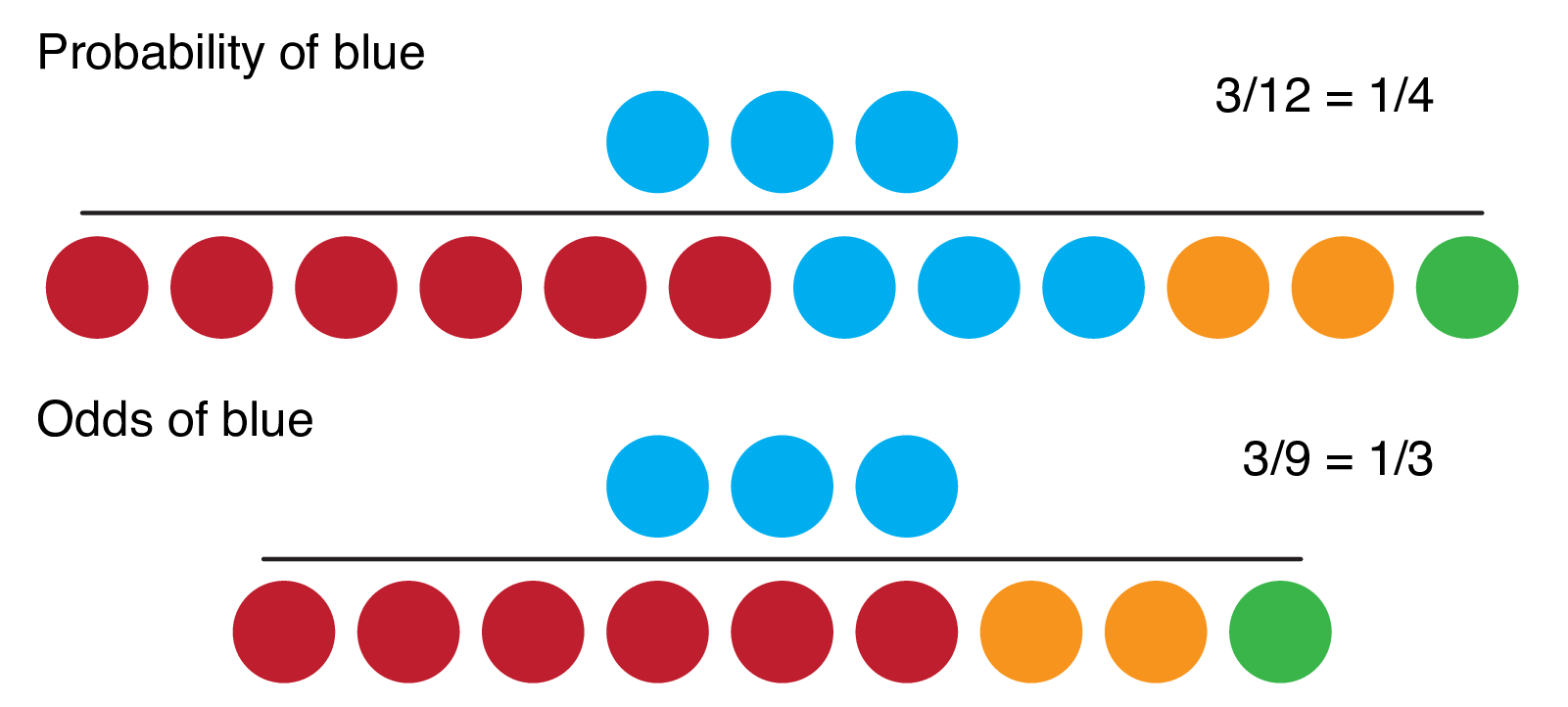
Odds, on the other hand, are the ratio of favorable outcomes to unfavorable outcomes The denominator contains ONLY the marbles that aren't the favorable outcomes Odds uses the contexts of good outcomes and bad outcomes Written as fractions, these two values are completely different Probability is 1/4 while odds in favor are 1/3 The differences between odds and probability are discussed in the points given below The term 'odds' is used to describe that if there are any chances of the occurrence of an event or not As against, While odds are expressed in the ratio, the probability is either written in percentage form or An odds is the ratio of the probability of an event to its complement $$\text{odds}(X) = \frac{P(X)}{1P(X)}$$ An odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of an event in one group (say, $A$) versus the odds of an event in another group (say, $B$) $$\text{OR}(X)_{A\text{ vs }B} = \frac{\frac{P(XA)}{1P(XA)}}{\frac{P(XB)}{1P(XB)}}$$



2 Odds Ghci Grade 12 Mathematics Of Data Management




Probability Odds Odds Ratio Youtube
As nouns the difference between odds and probability is that odds is the ratio of the probabilities of an event happening to that of it not happening while probability is the state of being probable;Odds, are given as (chances for success) (chances against success) or vice versa If odds are stated as an A to B chance of winning then the probability of winning is given as P W = A / (A B) while the probability of losing is given as P L = B / (A B) For example, you win a game if you pull an ace out of a full deck of 52 cards If you are confused about the difference between probability, chance, and odds, you're not aloneIn their paper Confusion Between Odds and Probability, a Pandemic?1, Fulton et al surveyed eight online dictionaries (including Cambridge, Macmillan, and MerriamWebster), and found that while they all defined probability in a similar way, all eight gave "inconsistent and




How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science
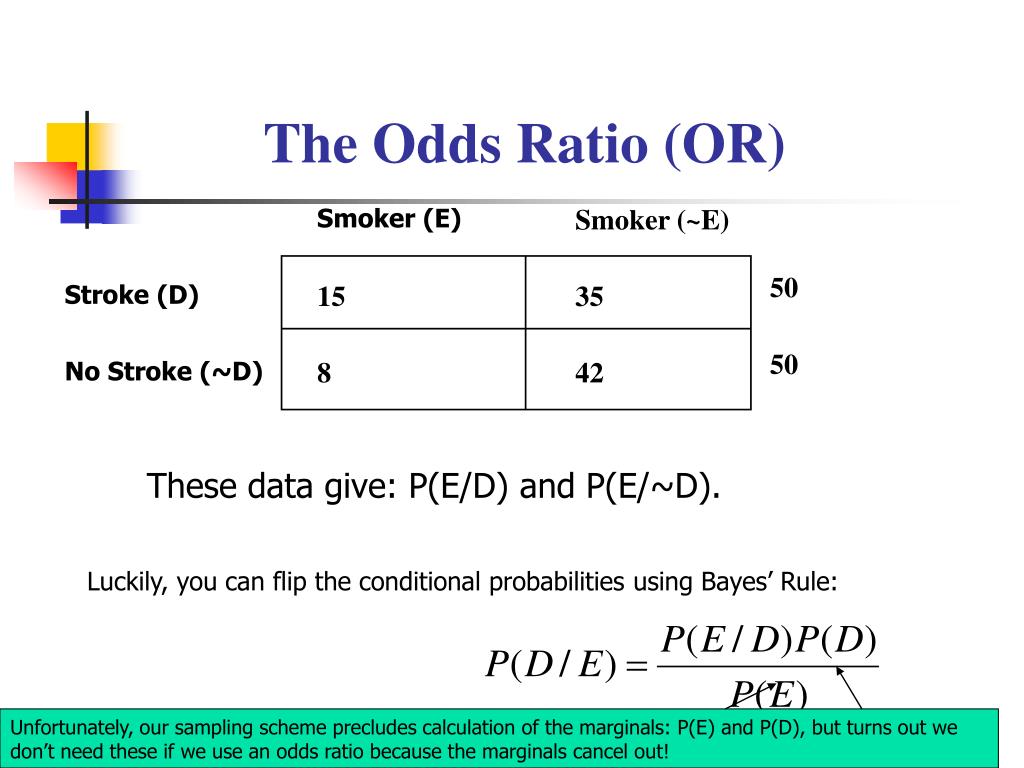
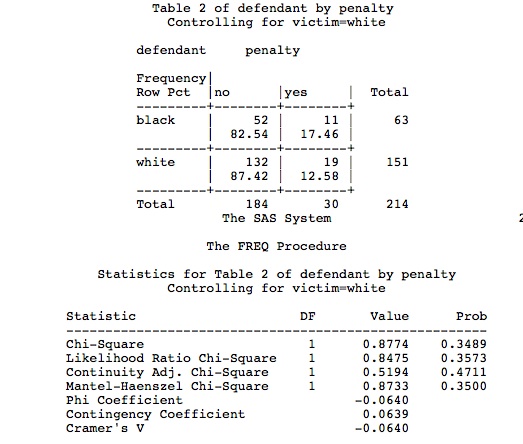
On the other hand, the odds ratio for blacks vs whites is 554/964 = 575, which says the odds for referral of blacks is only 575% of the referral odds for whites The relative risk and odds ratio numbers connote quite different magnitudes of difference between blacks and whites Odds ratios escalate dramatically beyond probabilities of 85Suppose we know that the probability of a female getting into a program are p = 7 and q = 1 − 7 = 3 for males Then we know odds ( female) = 7 / 3 = odds ( male) = 3 / 7 = We could use this information to compute an odds ratio Converting between odds and probability Converting Odds to Probability Simply add the 2 components of the odds together to make a new denominator, and use the old numerator eg If the odds are 35, or 3 to 5, the probability is 3 ÷ (35) = 3/8 = 375% Converting Probability to Odds Take the probability, and divide it by its compliment




Relative Risk Wikipedia



Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube
Difference Between Odds and Probability Odds vs Probability Probability is a mathematical assumption of chance that can be calculated using an equation The equation measures the chances for an event to occur against the total number of chances that occurrence may produce That is (Chances for)(Total Chances) Odds, on the other hand, are a measure of chance Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;Let's begin with probability Probabilities range between 0 and 1 Let's say that the probability of success is 8, thus p = 8 Then the probability of failure is q = 1 – p = 2 Odds are determined from probabilities and range between 0 and infinity Odds are defined as the ratio of the probability of success and the probability of




Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Formats For P Values And Odds Ratios In Sas The Do Loop
I hope this is posted in the right spot if not please just let me know and I'll remove it Anyways I'm a filmmaker and I'm making a film It's a ratio of events to nonevents You can switch back and forth between probability and odds—both give you the same information, just on different scales If O1 is the odds of event in the Treatment group and O2 is the odds of event in the control group then the odds ratio is O1/O2 Odds has an infinite range The probability of something happening is always less than the odds of it happening (assuming the probability is nonzero) The smaller the probability, the more similar probability and odds will be For example, the probability of winning the UK National Lottery is




Odds Ratio Wikiwand



The Difference Between Probability And Odds
If you are confused about the difference between probability, chance, and odds, you're not aloneIn their paper Confusion Between Odds and Probability, a Pandemic?1, Fulton et al surveyed eight online dictionaries (including Cambridge, Macmillan, and MerriamWebster), and found that while they all defined probability in a similar way, all eight gave "inconsistent andProbabilities of 0 are the same as odds of 0 If the probability is between 0 and 05, the odds will be below 10 If the probability is exactly 05, then the odds are 10 Think of flipping a coin; The relative risk of losing weight by choosing diet A over diet B is 1125, while the odds ratio is about 225 The reasons a medical article might choose one method of reporting over the other are complex, but the message here is that sorting that out starts by being clear about the difference between probability and odds
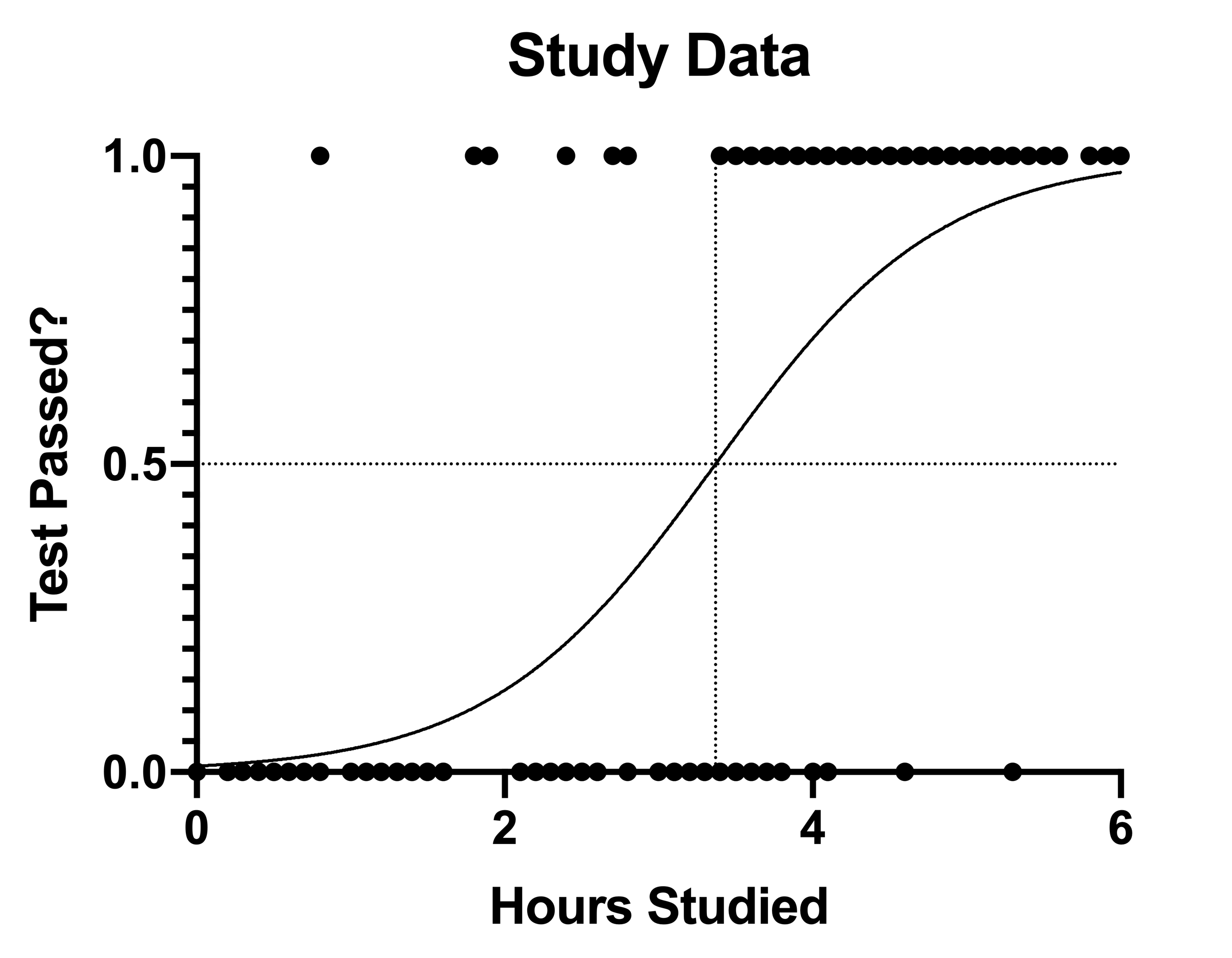



Graphpad Prism 9 Curve Fitting Guide Example Simple Logistic Regression




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
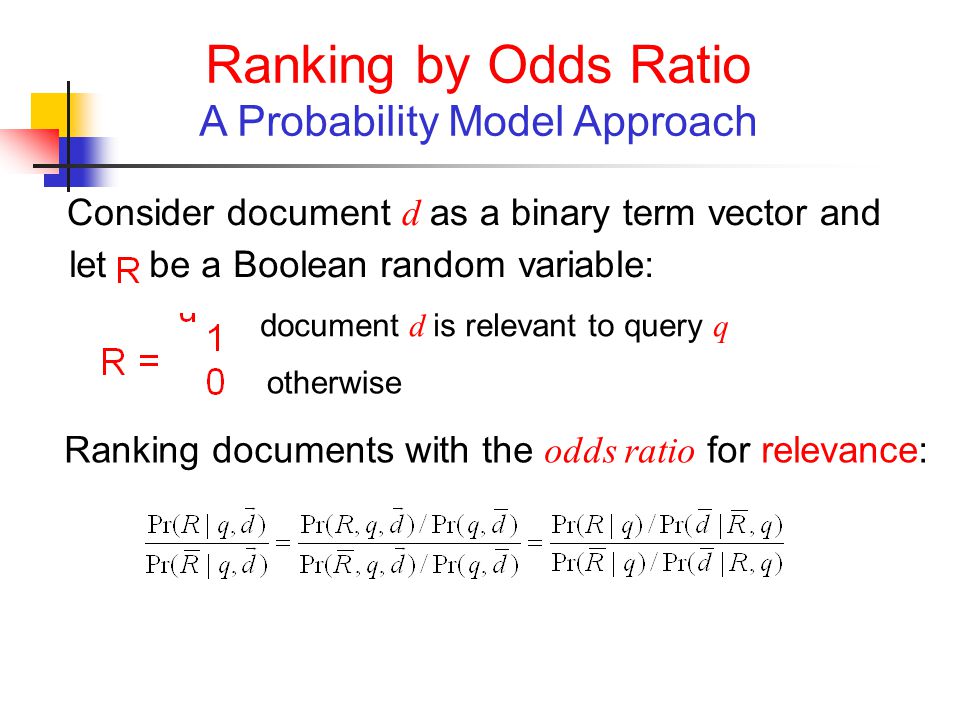



Ranking By Odds Ratio A Probability Model Approach Let Be A Boolean Random Variable Document D Is Relevant To Query Q Otherwise Consider Document D As Ppt Download



1




Lecture3
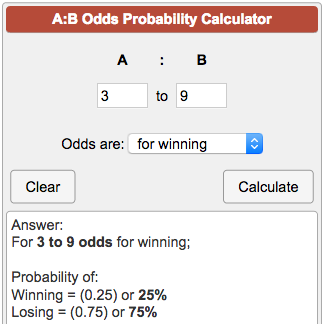



Odds Probability Calculator




How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




Fischer S Exact Test Odds Ratio And Confidence Intervals Jmp User Community



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




Example 8 29 Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios R Bloggers




Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube



Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



Odds Likelihood Ratios Guide To Diagnostic Tests




Odds Ratio Sage Research Methods




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



What Are The Odds Stats With Cats Blog




Summary Of Odds Ratios Logarithmic Scale And Probability Of X 2 For Download Table




Ppt Odds Vs Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Estimates Of Odds Ratios Of Daily Probability Of Diarrhea In The Download Scientific Diagram



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau



1




Ppt Conditional Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Estimated Z Score Odds Ratio And The Corresponding Probability For The Download Table



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsrisk




Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science




Part 3 Module 3 Probability Suppose We Create




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




R Calculate And Interpret Odds Ratio In Logistic Regression Stack Overflow




Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper




File Preventive Medicine Statistics Sensitivity Tpr Specificity Tnr Ppv Npv Fdr For Accuracy Likelihood Ratio Diagnostic Odds Ratio 2 Final Wiki Png Wikimedia Commons




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



5 3 Marginal And Conditional Odds Ratios Stat 504
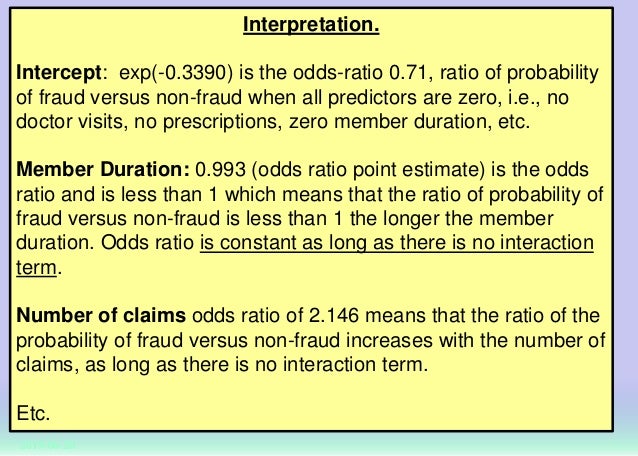



Classification Methods And Assessment




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




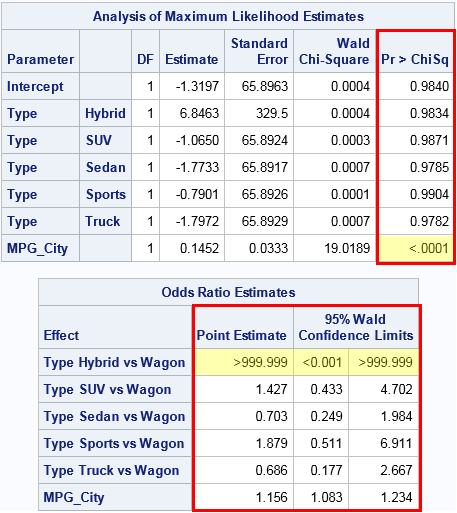
Re 999 999 Odds Ratio In Logistic Regression M Sas Support Communities




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




Binary Logistic Regression With Odds Ratios Calculated For The Download Table




What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science




Likelihood Ratio And Odds Ratio Slope Values Represent Odds As Shown Download Scientific Diagram
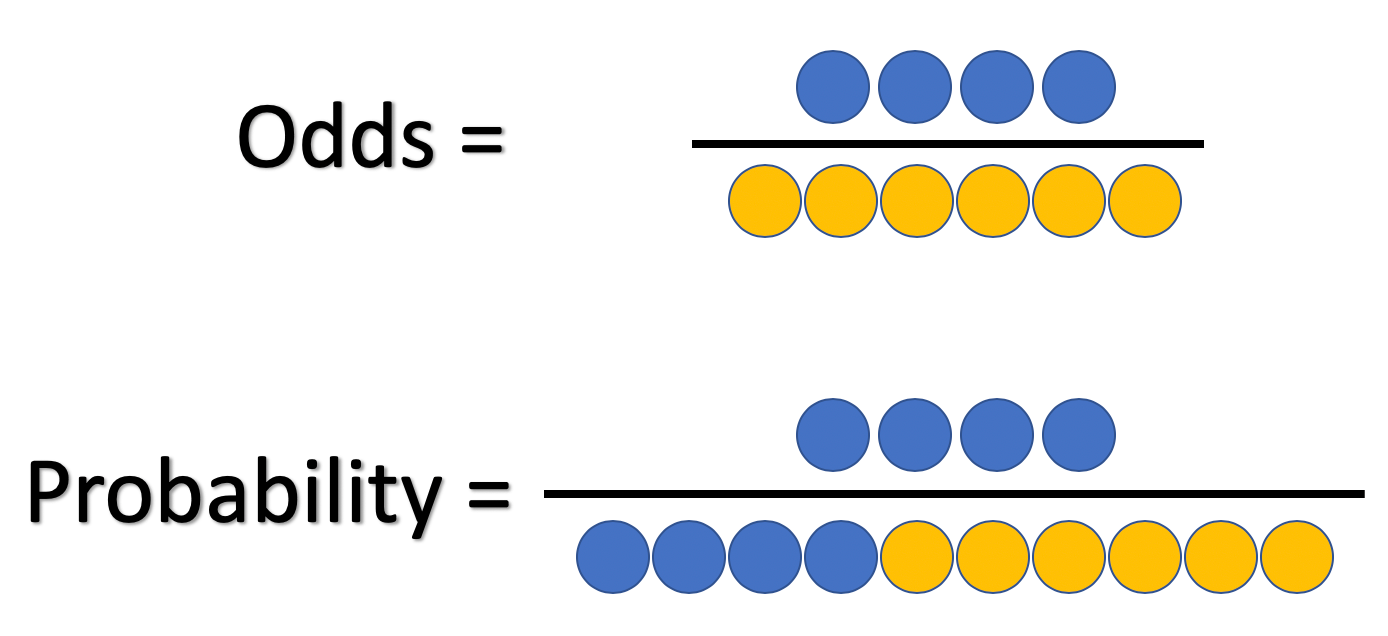



What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube
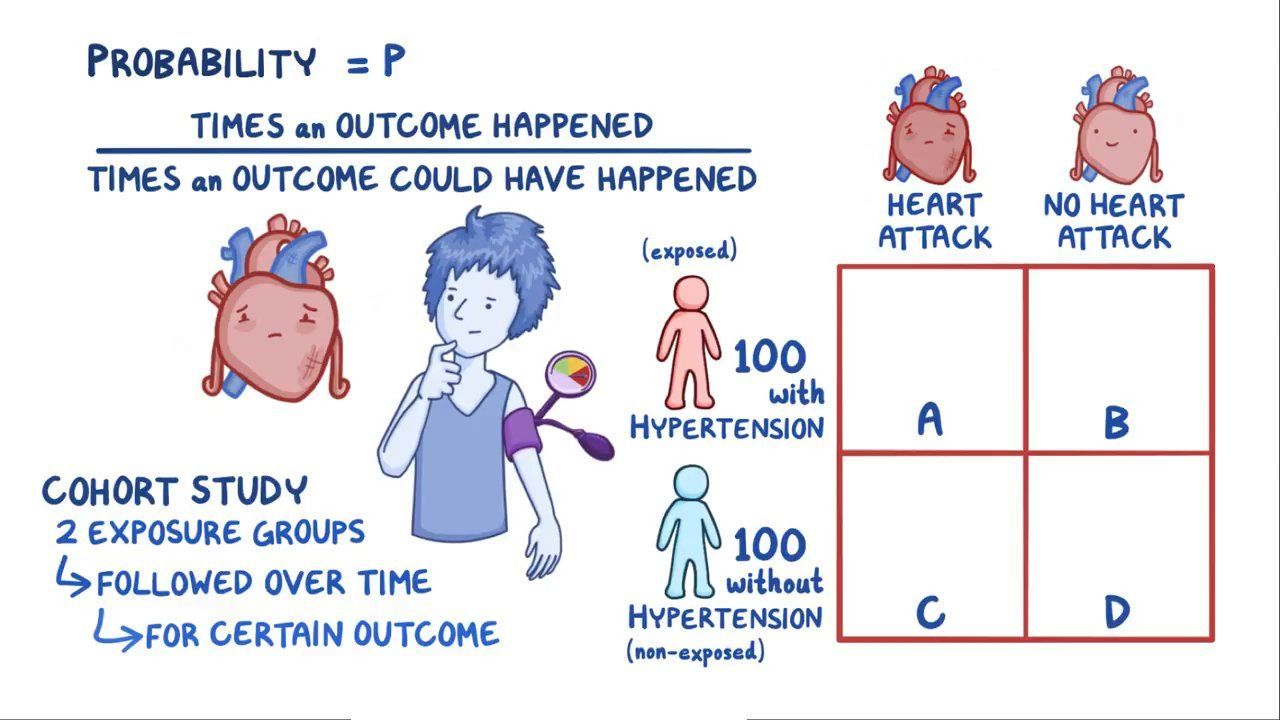



Odds Ratio Osmosis




Interpreting Mlogit Coefficients In R Odds Ratios And Negative Coefficients Cross Validated




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Lecture3



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios
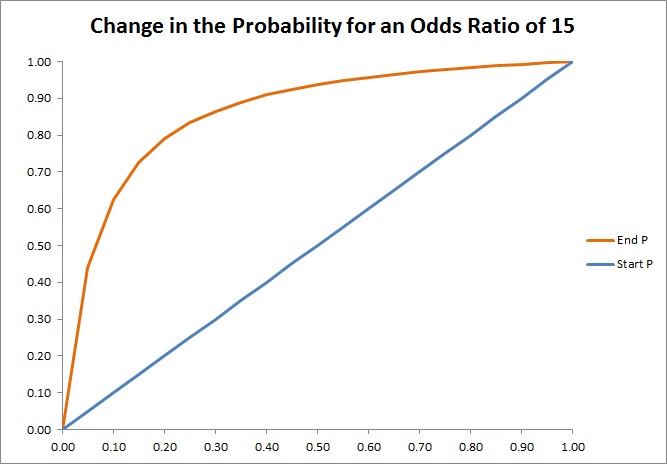



How To Convert Odds And Units To Probability Convert Odds To Percentage




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



1



Odds Ratios Basic Concepts




9 6 Odds To Probabilities 1 If The Odds Of An Chegg Com




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Converting Between Probability And Odds Mathwoes Youtube



Proportions Chi Squared Tests And Odds Ratios




Probability Vs Odds Youtube




Webinar Recording Signup




Statistics 12 Probability Vs Odds Stats Seandolinar Com




Epi546 Block I Lecture 3 Frequency How Do




Odds Ratio Relative Risk




1 A Comparison Of Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio With The Average Marginal Download Scientific Diagram



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




Probability And Odds Pptx Powerpoint



Proc Logistic And Logistic Regression Models




Probability Vs Odds What S The Difference Learn It And By Z Ai Towards Data Science




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_The_Math_Behind_Betting_Odds_and_Gambling_Nov_2020-01-735accb453c8424b9e063c2c14e4edf4.jpg)



The Math Behind Betting Odds Gambling



Odds Ratio For A Simple Distribution Jmp User Community




How To Calculate Odds Ratios And Probabilities In Case Control Studies Cross Validated




Odds Vs Probabilities Odds Ratio In Spss Exp B Is An Odds Rather Than A Probability Odds Success Failure Probability Likelihood Of Success For Ppt Download




Odds Ratio Sage Research Methods




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




What S The Difference Between Probability And Odds



Odds Likelihood Ratios Guide To Diagnostic Tests



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿